The eFPGAsim-based motor Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) testing system is a high-precision FPGA solution for HIL applications. Utilizing eHS (Electric Hardware Solver) technology, it delivers the high-speed and high-accuracy benefits of FPGA-based on-chip simulation while freeing engineers from the complexity of writing FPGA hardware code.

■ Can emulate abnormal operating conditions of different IGBTs and diodes, as well as various IGBT faults.
■ Can maintain stator voltage.
■ Can set rotor speed.
■ Can directly supply an internal sine wave to the motor drive.
■ Can generate internal PWM with dead-time for the inverter.
■ Can change motor resistance / Ld / Lq and flux values in real time.
■ Enables rapid hardware I/O layout design via GUI.
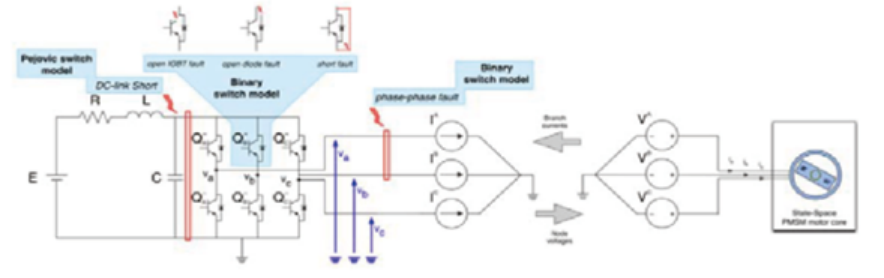
■ Limitations of Traditional Simulators
CPU runs the model; FPGA manages I/O.
■ Loop delay for CPU models reaches 20-30 µs.
■ For high-speed motor drive systems (PWM frequency > 10 kHz),
■ eFPGASim Simulation Solution
Architecture: CPU-run model or FPGA-run model. FPGA-run model achieves delay (1-2 µs).
With FPGA-run models, very small step sizes (< 1 µs) are achievable.
Dedicated solver facilitates decoupling.
FPGA manages I/O.
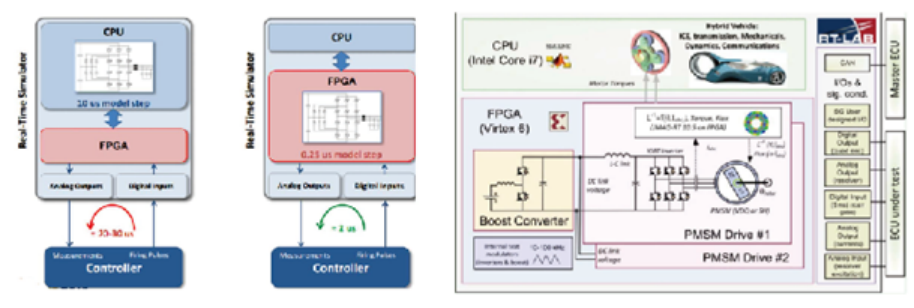
■ High-precision motor simulation models capable of emulating rotor asymmetry, harmonic back-EMF, magnetic saturation, IGBT dead-time effects, etc.
■ Includes a power electronics model library covering 2-level and multi-level inverters.
■ Supports real-time simulation of models from Simulink/SimPowerSystems.
■ Leverages EHS technology to enable high-precision co-simulation on CPU and FPGA, with simulation step sizes as low as 0.25 µs.
■ Suitable for control system development and testing requiring motor models.
■ FPGA-based high-speed I/O boards capable of processing high-speed AD/DA, static DIO, PWM, encoder, and resolver signals.
■ When testing critical protection circuits, the latency from external controller PWM signal acquisition to motor current signal output is below 1.3 µs.
Highprecision motor models are essential for achieving accurate closedloop testing in electric drive test systems. With years of engineering experience and OPALRT’s advanced solvers and models, we provide comprehensive motor model support—from functional verification to system testing and product development testing.
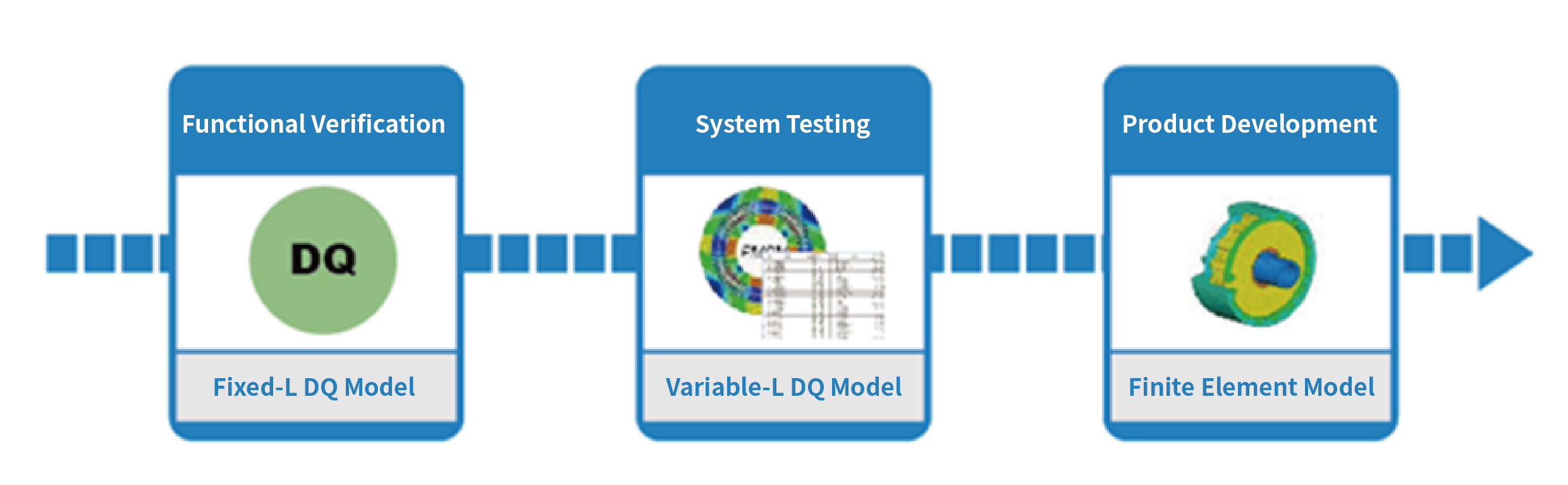
For a standard PMSM, the stator voltage under ideal conditions is sinusoidal, as are the backEMF and selfinductance. Using the rotor angle θ as a reference, the equations can be transformed via the Park transformation. The Park transformation (i.e., DQ transformation) converts sinusoidal variables such as selfinductance, flux linkage, and current into constants on the D and Qaxes, greatly simplifying analysis and control of the system.
Similar to the standard DQ PMSM model, the variable DQ model features Ld and Lq selfinductances that vary continuously with the operating point. At each operating point, Ld and Lq are updated directly using the Park transformation.
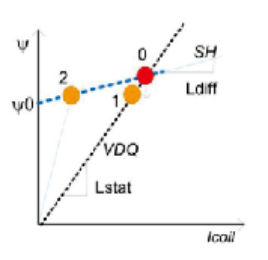
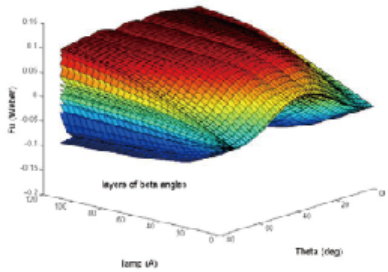
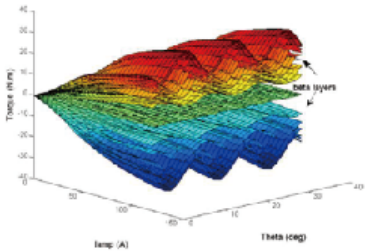
Highprecision model simulation can be used for performance optimization of highperformance motor control systems. The finite element motor model offers high accuracy by capturing the nonlinearity of the motor, which is equivalent to using true smallsignal characteristics across all operating points. This type of model is defined as a Spatial Harmonic (SH) model. SH curves are nonlinear and in some ways resemble saturationconversion models in EMTP. In cooperation with JSOL, we utilize JMAGRT to generate highprecision motor models. Combined with OPALRT’s FPGA technology, this enables even higherfidelity model simulation.